Apr 30 2024
/
What is AWG Cable
In the digital age, our world is connected through a complex network, and cables play a crucial role in keeping our data connections stable. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) cable is a key element in this connectivity puzzle, yet its full potential is often overlooked. For network administrators, IT professionals, and small business owners, understanding AWG cable is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted internet flow, akin to ensuring the lifeblood of your business runs smoothly.
Understanding AWG Cable and Why It Matters
A Conduit of Connectivity
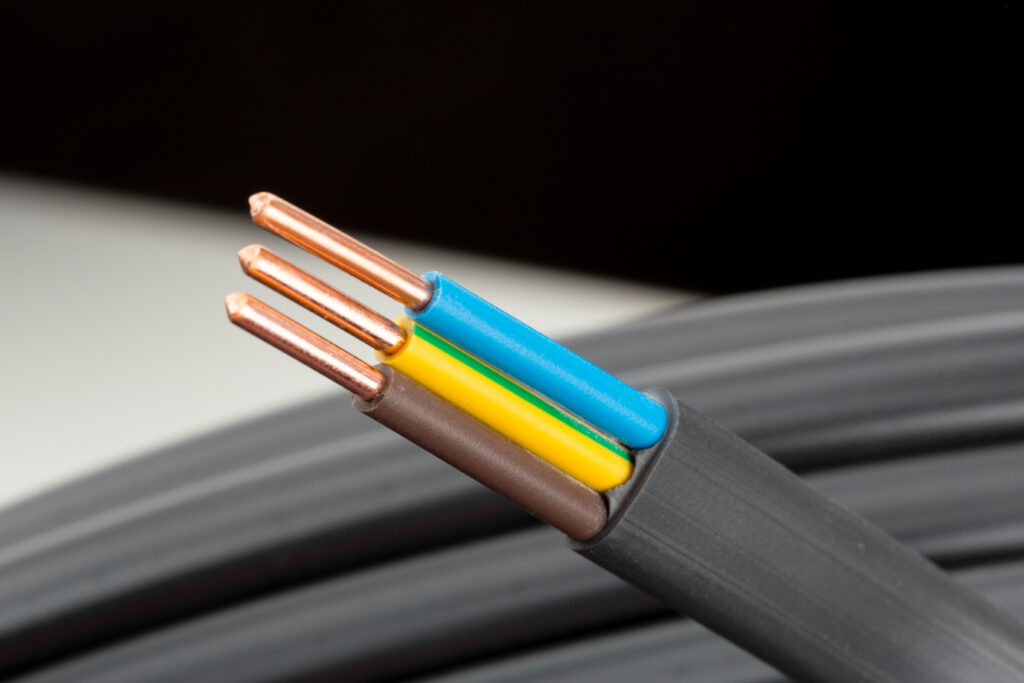
AWG cable, or wire gauge, is the standard for measuring conductor diameter in cables and wires. Simply put, a higher AWG number means a thinner wire. This detail is crucial because a wire’s thickness affects its electrical resistance. Thus, thicker cables can carry more current over longer distances with less loss.
In networking, AWG is vital. Data centers, businesses, and home offices depend on various AWG cables for different needs. Whether for Ethernet, PoE, HDMI, or USB connections, choosing the right AWG cable is key to a network’s stability, speed, and efficiency.
AWG Cables in Different Networking Scenarios
Ethernet Cables and Their Role
When setting up a local area network (LAN), the choice of Ethernet cables is pivotal. AWG directly impacts the category of the Ethernet cable and consequently its performance. For example, Cat5e cables typically use 24 AWG conductors, which provide good performance up to 100 meters. On the other hand, Cat6 cables may use thicker 23 AWG conductors to support higher bandwidths and power over Ethernet of up to 100 meters as well.
Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Considerations
With the proliferation of PoE devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points, understanding the AWG of your cables becomes crucial. When transmitting both data and power, the precise calculation and choice of AWG can prevent voltage drops and ensure the longevity of your devices.
HDMI and USB Cables
Entertainment systems and multimedia setups often rely on HDMI cables and USB connections to deliver high-definition content and link peripheral devices. These consumer applications also benefit from AWG awareness; a thicker cable like 22 AWG in HDMI can transport data with minimal degradation, offering superior picture and sound quality.
How to Choose the Right AWG Cable for Your Network
Consider Your Bandwidth Needs
The first consideration is your network’s current and future bandwidth requirements. Higher AWG cables support increased data transfer rates and can future-proof your network to some extent. With the advent of technologies like 4K streaming, IoT, and cloud computing, investing in a thicker cable might save you from a midstream upgrade.
Length of the Cable Run
The second factor is the length of the cable run. Longer distances demand lower AWG cables to mitigate signal loss. Planning your network infrastructure with these cable lengths in mind will lead to more reliable and cost-effective solutions.
Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations are also important. For outdoor or industrial settings, the cable’s robustness in the form of a thicker AWG, such as 18 or even 16 in direct-burial cables, can protect against moisture and physical damage.
Device Compatibility
Before making your purchase, ensure that the cables are compatible with your devices. Check PoE standards, the type of data transmission (analog vs. digital), and the supported cable categories against your AWG choices.
The Trade-off Between Cost and Performance
Calculating the Investment
While thicker AWG cables often promise better performance, they do come at a higher cost. Businesses need to calculate the value of that investment against their network efficiency and the avoidable costs of potential downtimes and equipment damage.
The Long-term Perspective
Adopting a long-term perspective can help you evaluate whether the initial investment in higher AWG cables aligns with your future costs. Will the thicker cable’s support of higher bandwidths and longer catenary serve you well as your network grows?
Best Practices for AWG Cable Installation
Attain Professional Expertise
In complex network setups, it’s wise to seek professional assistance. A network cabling expert can help design the installation, select the right cables, and implement best practices to ensure optimal performance.
Proper Termination and Pathways
The termination of your cables into connectors or switches is as important as the cable itself. Use quality termination equipment, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, and ensure proper cable management to prevent signal interference.
Testing and Maintenance
Even after installation, your cables will require periodic testing and maintenance. Tools like cable analyzers can help keep your network in top condition by identifying and rectifying any issues promptly.
The Future of AWG in Networking
Innovations in Cable Technology
As our reliance on network-based technologies grows, so too does the demand for more resilient and higher-performing cables. Manufacturers are continually innovating, offering new materials and designs to enhance the efficacy of AWG in modern networking applications.
Adapting to New Standards and Protocols
The evolution of networking standards and protocols will also influence the role of AWG in our networks. Keeping abreast of these changes and their implications for cable requirements is a must for any organization.
Developing an AWG Strategy
In conclusion, an understanding of the role AWG plays in networking is indispensable for anyone responsible for network integrity. Developing an AWG strategy that aligns with your infrastructure needs and future goals can be the difference between a network that merely survives and one that thrives.
Whether you’re upgrading your home office or leading the charge in a corporate setting, AWG cables deserve your consideration and respect. They are, after all, the lifeline of your network infrastructure – the thread that connects your world, one pulse of data at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does AWG stand for in networking cables?
AWG means American Wire Gauge, a system for measuring the diameter of wires in cables, affecting their current capacity and resistance.
How does AWG affect network performance?
AWG size impacts resistance and signal loss. Lower AWG numbers (thicker wires) offer less resistance and better signal over distances.
Can I use higher AWG cables for any network setup?
Higher AWG cables (thinner) are more flexible but may not suit every network, especially for longer distances or higher power needs. Consider flexibility, distance, and power.
Are there innovations in AWG technology?
Yes, there are ongoing innovations in cable materials and design to boost AWG cable efficiency, durability, and performance, including better shielding and conductor materials.
How often should I test and maintain my network cables?
Testing frequency should be based on use and environment. Initially test after setup and annually or more for busy networks.
How do new networking standards and protocols affect my AWG strategy?
New standards and protocols may demand higher data rates or reliability, requiring cables that meet these needs, possibly with higher quality or different shielding.