Apr 09 2025
/
IPv4 vs IPv6: What’s the Difference and Why Does It Matter?
The internet has become an integral part of our lives, but have you ever wondered how devices connect to each other and communicate seamlessly across the globe? It all boils down to IP addresses, specifically IPv4 and IPv6. These two protocols play a critical role in ensuring that our digital interactions happen flawlessly, but what are they exactly? And why does IPv6 exist when IPv4 has served us for decades?
This blog will explain everything you need to know about IPv4 and IPv6, their key differences, and why IPv6 represents the future of internet communication. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of these protocols and why transitioning to IPv6 matters.
What Is IPv4?
IPv4, short for Internet Protocol Version 4, is the fourth iteration of the IP protocol. It was introduced in 1983 and quickly became the backbone of internet communication.
How IPv4 Works
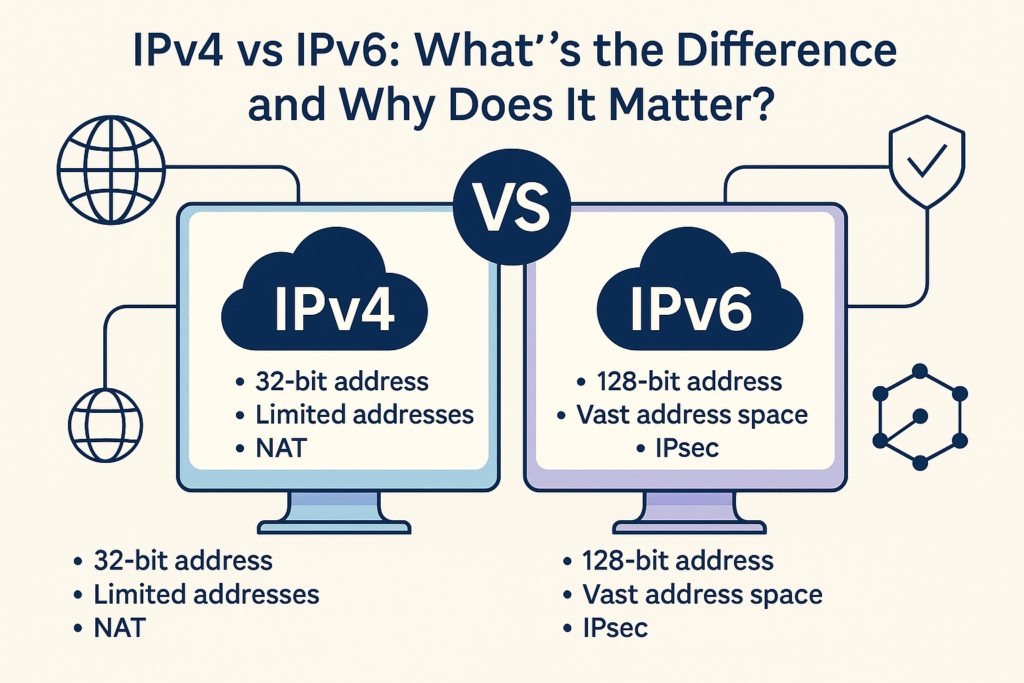
Every device connected to the internet needs an IP address to send and receive data. IPv4 addresses take the format of four groups of numbers (ranging from 0-255) separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.1. This format is called 32-bit addressing, which means there are approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses possible under IPv4.
IPv4 has been instrumental in shaping the internet as we know it. However, its success has also become a limitation. With the rapid growth of internet-connected devices, from smartphones and laptops to IoT devices, the available IPv4 addresses are running out.
Key Features of IPv4:
- Address Format: 32-bit (e.g., 192.168.x.x)
- Total Addresses: About 4.3 billion
- Widely Supported: Almost all devices and networks support IPv4.
- Simpler Configuration: Straightforward and easy to implement.
What Is IPv6?
IPv6, or Internet Protocol Version 6, is the next-generation protocol designed to overcome the limitations of IPv4. It was developed in the late 1990s by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as a solution to the rapid depletion of IPv4 addresses.
How IPv6 Works
Unlike IPv4, IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, which allows for an astronomical number of unique IP addresses (approximately 340 undecillion addresses). This ensures that there’s enough capacity to support not only the devices we use today but also emerging technologies of the future, such as autonomous cars, smart cities, and beyond.
IPv6 includes modern features to improve network efficiency, security, and scalability, making it an ideal replacement for IPv4 in the long term.
Key Features of IPv6:
- Address Format: 128-bit (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e) using hexadecimal notation.
- Total Addresses: Virtually limitless (340 undecillion).
- Enhanced Security: Built-in support for IPSec encryption.
- Improved Efficiency: Features like simplified packet headers and auto-configuration for easier management.
Key Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
Now that you know what IPv4 and IPv6 are, let’s break down how these protocols differ and why those differences matter.
1. Address Capacity
- IPv4: Supports approximately 4.3 billion addresses.
- IPv6: Supports 340 undecillion addresses. This is over 79 octillion times more than IPv4.
Why it matters: With the explosion of internet-connected devices, IPv6 ensures we won’t run out of IP addresses anytime soon.
2. Address Format
- IPv4: 32-bit addresses written in dotted-decimal notation (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6: 128-bit addresses written in hexadecimal and separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8::1).
Why it matters: The expanded address format allows IPv6 to handle growing demands without running out of unique identifiers.
3. Security
- IPv4: Security features are optional and require additional configurations.
- IPv6: Security is baked into the protocol with native support for IPSec, providing improved data integrity and confidentiality.
Why it matters: With cyber threats on the rise, IPv6 offers strengthened security to protect digital communications.
4. Efficiency
- IPv4 uses NAT (Network Address Translation) to conserve address space, which introduces inefficiencies.
- IPv6 eliminates the need for NAT, improving end-to-end connectivity and reducing latency.
Why it matters: IPv6 simplifies network configurations, allowing for faster communication and lower overhead.
5. Auto-Configuration
- IPv4 requires manual or DHCP-based configuration.
- IPv6 supports stateless address auto-configuration (SLAAC), allowing devices to self-configure.
Why it matters: This makes IPv6 networks easier to manage and reduces administrative overhead.
Why Is IPv6 Adoption Important?
While IPv4 is still widely used, the transition to IPv6 is inevitable due to its numerous advantages. Here’s why businesses and individuals alike should prioritize IPv6 adoption:
- Future-Proofing: IPv6’s vast address space ensures scalability as the number of connected devices continues to grow.
- Improved Performance: IPv6’s efficiency features, such as streamlined routing and header structures, translate to better network performance.
- Enhanced Security: With built-in encryption capabilities, IPv6 offers better protection against cyberattacks.
- Support for Innovation: Technologies like IoT, 5G, and smart cities rely on IPv6 to accommodate vast numbers of devices.
However, it’s important to note that IPv4 and IPv6 can coexist during the transition period. This is achieved through dual-stack configurations, where networks support both protocols simultaneously.
Should You Transition to IPv6?
If your organization hasn’t started planning its transition to IPv6, the time to act is now. Here are some steps to consider:
- Evaluate Your Infrastructure: Determine whether your existing hardware and software support IPv6.
- Train Your Team: Ensure your IT team is equipped to handle IPv6 deployments and configurations.
- Adopt Dual-Stack Configurations: Gradually transition by enabling both IPv4 and IPv6 on your network.
- Work with Partners: Collaborate with ISPs, cloud providers, and vendors who support IPv6.
Wrapping It Up
IPv4 has been a faithful servant since the dawn of the internet, but the limitations of its 32-bit architecture have become evident in the face of rapid digital expansion. IPv6 is the future, offering virtually unlimited addresses, enhanced security, and improved network efficiency.
Transitioning to IPv6 may seem daunting at first, but its benefits far outweigh the challenges. Whether you’re an individual, business, or organization, adopting IPv6 ensures you stay ahead in an increasingly connected world.
Are you ready to future-proof your network? Start planning your IPv6 transition today and secure your place in the next phase of the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is IPv6?
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, is the latest version of the internet protocol designed to replace IPv4. It provides an almost limitless number of IP addresses and helps accommodate the growing demand for internet connectivity.
2. Why is IPv6 important?
IPv6 is crucial because the available IPv4 address space is depleted. With the rise of IoT devices and expanding global internet usage, IPv6 ensures that devices remain connected without limitations.
3. How does IPv6 improve security?
IPv6 was designed with built-in security features, such as IPsec, which provide end-to-end encryption and authentication, making networks more secure.
4. Is transitioning to IPv6 difficult?
The transition can pose challenges depending on the scale of your network, but gradual planning and dual-stack implementation (using IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously) can simplify the process.
5. Do I need new hardware to support IPv6?
Many modern devices and routers already support IPv6. However, older hardware might require updates or replacement to handle IPv6 traffic.