Apr 09 2025
/
Understanding Cable Outer Diameter and Its Importance
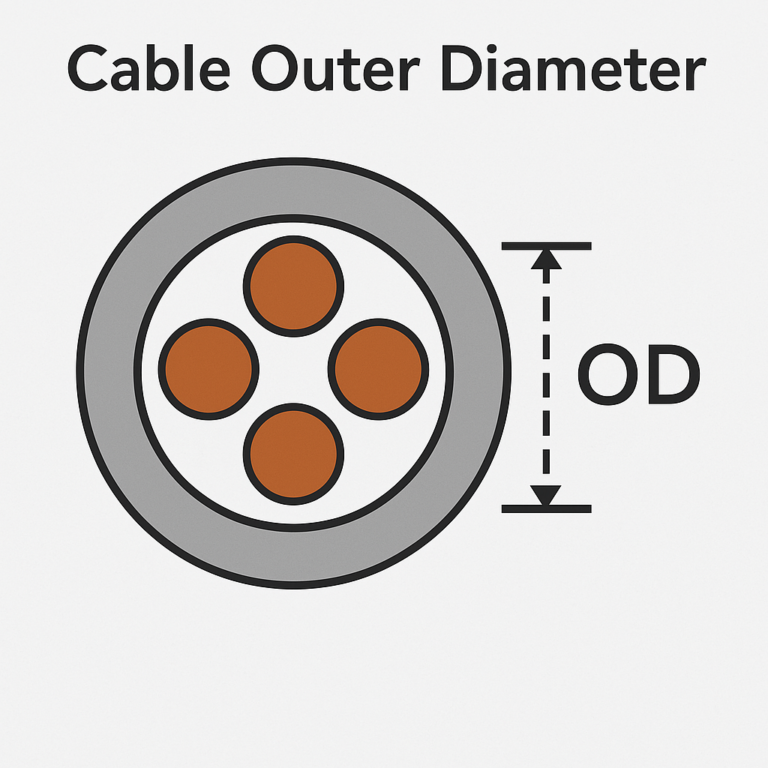
When selecting cables for your project, one crucial factor that often gets overlooked is the cable outer diameter (OD). The outer diameter of a cable may seem like a minor detail, but it has significant implications for performance, installation, and overall system reliability.
This article will cover everything you need to know about cable outer diameter, including why it’s important, how it’s measured, and the key considerations for choosing the right cables for your application. Whether you’re an engineer, electrician, or project manager, this guide will help you make informed decisions when dealing with cables.
What Is Cable Outer Diameter?
Cable outer diameter (often abbreviated as OD) refers to the thickness or the outside measurement of a cable, including all its layers. It is typically measured in millimeters or inches and accounts for the conductor, insulation, shielding, and the outer jacket.
Why Cable Outer Diameter Matters
The OD of a cable affects multiple aspects of its functionality, from physical installation requirements to overall performance. For example:
- Conduit and Installation: The OD determines whether a cable will fit into a conduit, raceway, or cable tray. A miscalculation in diameter can result in costly delays or design adjustments.
- Flexibility: Cables with smaller diameters are generally lighter and more flexible, making them suitable for applications with tight bends or uneven terrains.
- Weight and Load: Larger cables are usually heavier, which can put extra strain on supporting structures and increase shipping costs.
- Thermal Regulation: The diameter impacts how efficiently a cable dissipates heat. Larger diameters tend to handle higher currents but may require additional space for proper ventilation.
How Is Cable Outer Diameter Measured?
Measuring cable OD isn’t as simple as you might think, as various factors come into play. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Use Precision Measuring Tools: Tools like calipers or micrometers are typically used to measure the OD of a cable.
- Include All Layers: Ensure that measurements account for all layers of the cable, including insulation, shielding, and the outer jacket.
- Consider Acceptable Tolerances: Manufacturers often specify tolerances for cable diameters (+/- values). This means slight variations in diameter are normal and within acceptable limits.
- Verify Manufacturer Specs: Always cross-reference real-world measurements with the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure accuracy.
Common Standards for Cable OD
Cable diameters are measured according to various industry standards. Some common standards include:
- ISO/IEC guidelines for structured cabling systems.
- AWG (American Wire Gauge) standards, which correlate a wire’s diameter and current-carrying capacity.
- EN/IEC 60228, which specifies conductor sizes and tolerances for electrical cables.
Factors That Affect Cable Outer Diameter
The overall thickness of a cable depends on several design elements. Below are the main factors influencing cable outer diameter:
1. Conductor Material and Gauge
The core of the cable is typically made of copper or aluminum. Thicker conductors (lower AWG values) result in larger diameters and are used for high-current applications.
2. Insulation
Insulation is the layer protecting the conductor from short circuits and external interference. Common materials include PVC, Teflon, and polyethylene, and the thickness of this insulation directly affects the OD.
3. Shielding
Shielding provides protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). Types of shielding include foil, braided, or spiral layers, and each adds to the cable’s overall diameter.
4. Outer Jacket
The external layer, known as the jacket, protects the cable from environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. The choice of jacket material (e.g., rubber or PVC) and its thickness will impact the OD.
5. Cable Construction
The configuration of the cable, such as single-core vs. multi-core, also affects the OD. Multi-core cables tend to have larger diameters due to the number of individual conductors grouped together.
Choosing the Right Cable Based on Outer Diameter
When selecting a cable for your project, here are some key considerations related to its OD:
1. Application Requirements
Think about where the cable will be installed. For tight spaces or conduits, a smaller OD may be more practical. On the other hand, outdoor and industrial environments may require thicker outer jackets for durability.
2. Electrical Performance
Larger diameters often correlate with higher current-carrying capabilities. If your project involves heavy power loads, prioritize cables with a diameter suitable for the required amperage.
3. Compliance
Check if the cable meets the relevant industry standards for its intended use. This is especially critical for safety and code compliance in regulated industries like construction and manufacturing.
4. Future Scalability
If your system may grow, consider future cable additions or upgrades. Choosing cables with slightly larger diameters may simplify scaling without the need for new conduits or trays.
5. Budget Considerations
While cables with larger diameters may be necessary for performance reasons, they often come with a higher price tag. Strike a balance between quality, performance, and budget.
Challenges with Incorrectly Sized Cable OD
Using cables with the wrong outer diameter can lead to several issues, including:
- Cost Overruns: Replacing cables that don’t fit into conduits or trays can be an expensive and time-consuming process.
- Heat Build-Up: Overpacking a conduit with cables of larger OD may restrict air circulation, increasing the risk of overheating.
- Reduced Lifespan: Excess strain on the cable from unsuitable fittings can lead to physical damage and reduced durability.
Tools to Determine Cable Outer Diameter Quickly
If physical measurement isn’t practical, there are tools and resources available to simplify the process:
- Manufacturer Specifications: Always check the datasheet for precise OD measurements.
- Cable Sizing Tools: Online calculators or tools (offered by manufacturers) help estimate which cables will fit into specific enclosures or pathways.
- Software Solutions: Design software like AutoCAD includes features to visualize cable pathways and plan for appropriate diameters.
Wrapping It All Up
The outer diameter of a cable may seem like a small detail, but its impact is far-reaching. From installation logistics and thermal management to safety and compliance, understanding OD is essential for making informed decisions.
The next time you’re selecting a cable, don’t just focus on the technical specifications like voltage and current ratings. Take a closer look at the outer diameter and ensure it aligns with your project’s needs.
By mastering the basics of cable OD, you’ll avoid costly mistakes, improve system reliability, and ensure a smoother project rollout.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is cable outer diameter (OD)?
The outer diameter of a cable refers to the total width of the cable, including all its layers such as insulation, shielding, and outer jacket. It’s a critical measurement to ensure compatibility with connectors, conduits, and cable trays.
2. Why is cable OD important?
Cable OD impacts installation, performance, and safety. An incorrect OD can cause fitting issues, overheating, or mechanical stress when placed in conduits or cable management systems.
3. How is cable OD measured?
Cable OD is typically measured using calipers or specialized tools designed for precise diameter measurements. Manufacturers also provide OD specifications for each cable type.
4. Can cable OD affect current capacity?
Indirectly, yes. While OD itself doesn’t determine current capacity, it is related to the cable’s construction and insulation, which do influence the maximum current the cable can handle.
5. What should I consider when choosing cable OD?
Consider the available space for installation, compatibility with connectors, voltage and current ratings, and the environmental conditions the cable will be exposed to. Always verify specifications for your project to avoid potential issues.