May 28 2024
/
What is the use of a media converter?
In the dynamic realm of networking technology, maintaining an efficient and adaptable infrastructure is vital for businesses of all sizes. Here enters the media converter—a versatile device that bridges the gap between various types of network media, ensuring seamless data transmission across diverse environments. But what exactly does a media converter do, and how can it enhance your network? In this comprehensive guide, we explore the core functions, types, and advantages of media converters, underscoring their significance in today’s digital age.
What is a Media Converter?
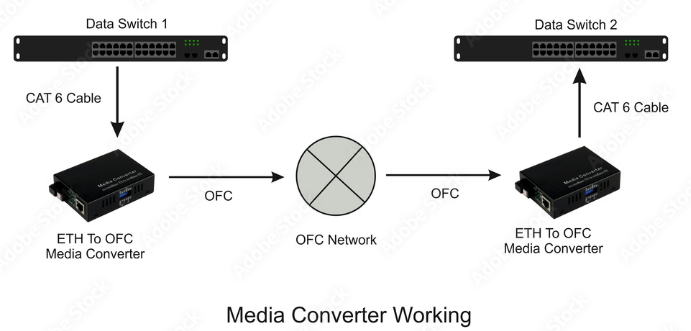
A media converter is a networking device designed to connect different types of media, such as twisted pair copper cables and optical fiber cables. These devices essentially translate the signal from one type of media to another, enabling smooth data communication across varied network infrastructures. Media converters are particularly useful in extending the reach of networks, enhancing performance, and providing greater flexibility in network design.
Core Functions of Media Converters
- Media Translation: The primary function of a media converter is to convert the data signals from one type of media to another. For example, it can convert signals from copper Ethernet cables to fiber optic cables, and vice versa.
- Network Extension: By converting copper to fiber, media converters allow for data transmission over longer distances than copper cables alone can support, significantly extending the reach of a network.
- Signal Boosting: Media converters can regenerate and amplify signals, ensuring data integrity is maintained over extended distances.
- Speed Bridging: These devices can also bridge the speed gap between different network segments, enabling compatibility between high-speed fiber networks and slower Ethernet segments.
Types of Media Converters
Media converters come in several types, each designed for specific networking needs and environments. Here are some common types:
1. Fiber-to-Fiber Media Converters
These converters are used to connect two different types of fiber optic cables, such as single-mode to multimode fiber or dual-fiber to single-fiber. They are often employed to extend the reach of fiber networks and to integrate newer fiber technologies into existing infrastructures.
2. Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
Copper-to-fiber media converters are among the most commonly used types. They connect copper-based Ethernet networks to fiber optic networks, allowing for increased transmission distances and improved network performance. These are particularly useful for linking different floors of a building or connecting geographically separated offices.
3. Telecommunications Media Converters
Designed for telecom applications, these converters are used to integrate legacy TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) circuits with modern IP-based networks. This type of converter is essential for telecom operators looking to upgrade their infrastructure without completely overhauling their existing systems.
4. Industrial Media Converters
Built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, industrial media converters are used in settings like manufacturing plants, transportation systems, and outdoor installations. They are ruggedized to resist extreme temperatures, humidity, and mechanical stress.
Key Advantages of Using Media Converters
Implementing media converters within your network infrastructure can offer numerous benefits:
1. Extended Network Reach
One of the most significant advantages of media converters is their ability to extend network reach. Fiber optic cables support much longer transmission distances compared to copper cables. By converting copper signals to fiber, media converters enable data transmission over greater distances without compromising signal quality.
2. Cost-Effective Upgrades
Media converters provide a cost-effective solution for upgrading existing network infrastructure. Instead of replacing entire cable runs with expensive fiber optics, media converters allow for the integration of fiber segments into existing copper-based networks, minimizing costs and disruptions.
3. Enhanced Network Performance
Fiber optic cables offer higher bandwidth capabilities and are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) than copper cables. By incorporating media converters, businesses can leverage these advantages to enhance overall network performance, reduce latency, and improve data transfer speeds.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
Media converters offer unparalleled flexibility in network design. They support a variety of network topologies and can easily integrate with different networking equipment. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses anticipating future growth, as media converters can be easily scaled to accommodate expanding network requirements.
5. Seamless Integration
Media converters facilitate the seamless integration of disparate network segments. They enable compatibility between different media types and network speeds, ensuring smooth communication across diverse networking environments.
Real-world applications of Media Converters
Media converters find applications in various industries and scenarios, reflecting their versatility and critical role in modern networking. Here are a few examples:
1. Enterprise Networks
In large corporate environments, media converters are used to connect office buildings, data centers, and remote locations. They enable efficient data transmission over long distances, supporting high-speed communication between geographically separated sites.
2. Telecommunications
Telecom operators use media converters to bridge older TDM circuits with modern IP networks. This allows for gradual infrastructure upgrades while maintaining service continuity.
3. Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, media converters are essential for connecting machinery and control systems across a factory floor. Their rugged design ensures reliable performance in harsh conditions.
4. Campus Networks
Universities and educational institutions use media converters to link multiple buildings and create unified campus-wide networks. This enables seamless data sharing and collaboration among students and faculty.
5. Surveillance Systems
Media converters are used in surveillance systems to connect IP cameras to central monitoring stations over long distances. This ensures high-quality video transmission and reliable security monitoring.
Choosing the Right Media Converter
Selecting the appropriate media converter for your network depends on several factors, including the type of media you’re connecting, the distance of transmission, and the specific requirements of your application. Here are some key considerations:
- Compatibility: Ensure the media converter is compatible with the networking equipment and cables you’re using.
- Distance: Consider the distance over which data needs to be transmitted. Choose a media converter that supports the required transmission range.
- Environment: For industrial or outdoor applications, opt for ruggedized media converters designed to withstand harsh conditions.
- Speed: Match the media converter with the required network speed to ensure optimal performance.
- Scalability: If you anticipate future network expansion, choose a media converter that can be easily scaled to accommodate growing needs.
Conclusion
Media converters play a pivotal role in modern networking, offering a range of benefits—from extending network reach and enhancing performance to providing cost-effective upgrades and seamless integration. By understanding their functions, types, and applications, businesses can leverage media converters to create more efficient, flexible, and scalable network infrastructures.
As technology continues to evolve, the significance of media converters in bridging diverse media types and boosting network performance will only increase. Whether you’re deploying a new network or upgrading an existing one, incorporating media converters can help you build a robust, future-proof network that meets the demands of today’s digital landscape.
For further insights and expert advice on optimizing your network infrastructure, be sure to follow our blog. If you’re ready to explore how media converters can benefit your business, contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive range of networking solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a media converter?
A: A media converter is a device that enables communication between different media types, like copper and fiber optic cabling, allowing data transmission across varied network segments.
Q: When should I use a media converter?
A: Media converters are perfect for extending network distances, connecting different network types, and upgrading infrastructure without replacing existing cabling. They are useful where both fiber and copper cabling are needed.
Q: What types of media converters are available?
A: There are copper-to-fiber, fiber-to-fiber, and copper-to-copper converters. They can also be categorized by speeds such as Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet converters.
Q: How do I choose the right media converter for my network?
A: Consider the type of media, transmission range, environmental conditions, network speed, and scalability when choosing a media converter. Evaluating these factors ensures you pick one that meets your needs.
Q: Can media converters be used in outdoor environments?
A: Yes, ruggedized media converters are designed for harsh industrial and outdoor conditions. They can withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to elements, ensuring reliable performance.
Q: Are media converters easy to install and configure?
A: Most media converters feature plug-and-play functionality, making installation and configuration quick and easy, minimizing setup time and complexity.
Q: What are the benefits of using media converters?
A: Media converters extend network reach, improve performance, enable integration of different media types, and offer cost-effective upgrades. They provide flexibility and scalability for network expansion.